
Read all the related documents carefully before investing. Investment in securities market are subject to market risks.
WHATS MORE LIQUID NOTES PAYABLE OR ACCOUNTS PAYABLE PROFESSIONAL
Should you need such advice, please consult a professional financial or tax advisor. The content in these posts/articles is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as professional financial advice. The blog posts/articles on our website are purely the author’s personal opinion. The quick ratio and cash ratio also depict the relationship between current assets and liabilities. The higher the ratio, the higher the company’s ability to clear its liabilities. The current ratio is obtained by dividing current assets by liabilities. Current liabilities are used along with current assets to determine the solvency of a company. Accounts payables, bank overdrafts, etc., are some examples of current liabilities. ConclusionĬurrent liabilities depict a company’s short-term obligations. Additionally, the current ratio, quick ratio and cash ratio are some of the ratios that define the relationship between current assets and current liabilities. For instance, accounts payable are paid off using cash. They help in determining the short-term future requirements of cash for a company.Īlso, current liabilities are mostly paid off using the current assets, i.e., short-term assets of the company. The relationship between current assets and current liabilities is that both help in assessing the liquidity and solvency position of the company. Relationship between current liabilities and current assets Some examples of current assets are-Ĭurrent assets are debited in the journal entry and shown under assets on the balance sheet of a company. What are current assets?Ĭurrent assets are short-term assets of a company that can be converted into cash in the short run. In the same light, a low current ratio may be due to the company’s goodwill, thus its ability to have longer accounts payable cycle as compared to the accounts receivable cycle. Also, higher inventory levels may sometimes contribute to a high current ratio. For instance, a company may have high accounts receivable, which shows that the company is not efficient in collecting the debt. However, the current ratio does not fully represent a company’s short-term solvency. A comparatively lower current ratio shows that the company is risky and has a high likelihood of default. A high current ratio depicts that the management is efficiently utilising the current assets and resources are not lying unused. This ratio can be calculated in the following way-Ĭurrent ratio = Current assets / Current liabilitiesĭifferent industries have different current ratio values. The current ratio can also be termed the working capital ratio. It defines a company’s ability to pay off its short-term obligations. The current ratio measures a company’s short-term liquidity. Dividends payable are those that are due to be paid but are unpaid. These arise strictly from the operating activities of the business.ĭividends are a portion of the profits distributed to stakeholders. It is the money payable to the suppliers or vendors of a business. It is the money a business receives even though the goods have not yet been provided.
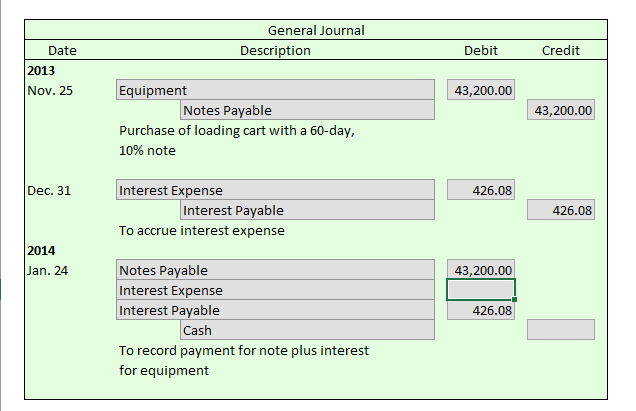
These are expenses that have been incurred/accrued but have not been paid off-for example, outstanding rent, interest payable, unpaid bills, etc. These are basically short-term loans taken by the business to meet its immediate requirements. Some current liabilities that are listed on the balance sheet are. What are some current liabilities listed on a balance sheet? Some examples of current liabilities include accounts payable to suppliers, bank overdrafts, unpaid expenses, unearned revenue, short-term loans, etc. So, the entry for this transaction would be Inventory A/C debited to Accounts Payable A/C. However, the company has not paid its supplier Z. Assume Company Y is a trading business and has an inventory worth Rs. The outstanding rent is then shown in the balance sheet as the current liabilities of the company. So, the accounting entry for this transaction would be – Rent A/C debited to outstanding Rent A/C. For example, assume Company X has an outstanding rent due after three months. Some examples of current liabilities are- accounts payable, short-term debt, outstanding rent, etc.Ĭurrent liabilities are credited in the books of accounts with the appropriate expense or asset account being debited.Current liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet.Current liabilities are the short-term commitments of a company that need to be paid within the operating cycle of the business.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
